#statusMessage#
Do you want to start the compare now?
#statusMessage#
Do you want to start the compare now?

Our electromagnetic environment is heavily burdened due to the multitude of transmitters and sources of interference pre...
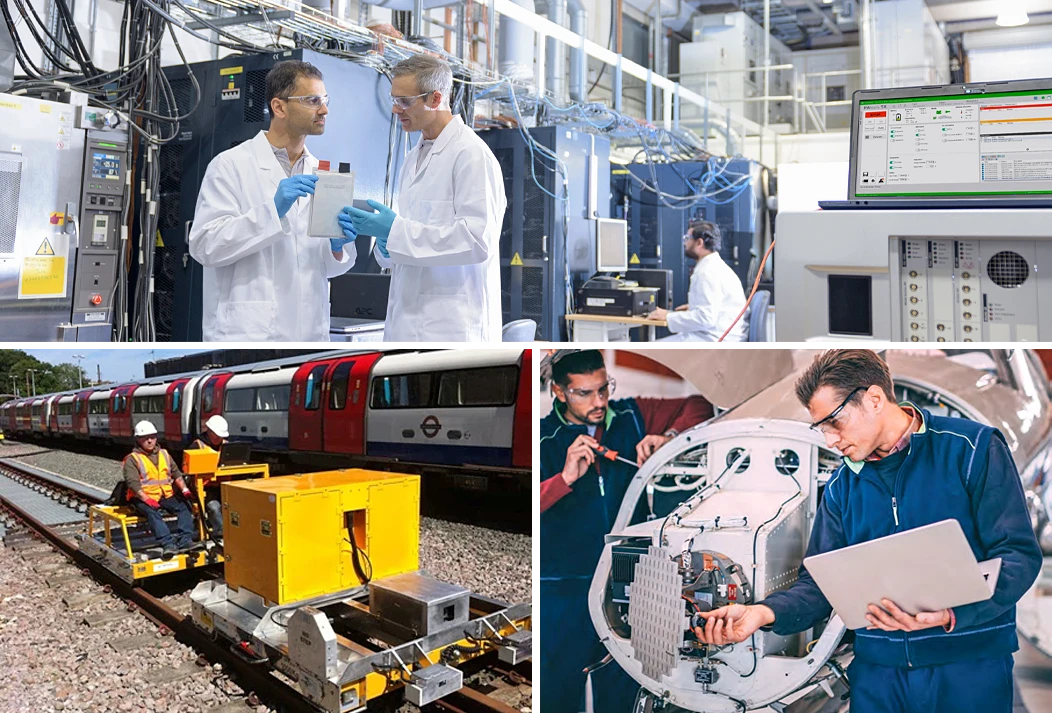

Automated test and measurement systems that are fully connected with instrumentation and test data can significantly inc...

Temperature is one of the most common risk factors in industry. Overheating can disrupt processes, reduce quality or cau...
Electric vehicles are the future - but what happens to the batteries when they can no longer be used in cars? Efficient ...
Immerse yourself in the world of power supplies and deepen your knowledge. Our experts are ready to guide you through all aspects of power supply usage. Get an overview of our product range.
Various types of power supply units are used in measurement technology to provide electrical energy and operate electronic devices.
The choice of a suitable power supply unit depends on various factors that are dictated by the specific requirements of the application. These steps should be taken into consideration when selecting a power supply unit:
Challenge us and send your own question to
frag‑uns[at]datatec.eu
We look forward to hearing from you!
The output power of a power supply unit describes the maximum electrical power that the power supply unit can supply to the connected load. It is the product of the output voltage and the output current and is usually measured in watts (W).
The formula for calculating the output power is as follows:
Output power = output voltage × output current
Laboratory power supply units and conventional power supply units differ in several aspects. Above all, laboratory power supplies offer greater functionality, accuracy and controllability for demanding applications and are often specially tailored to the needs of research and development. Conventional power supply units are designed more for general power supply requirements and everyday use. The most important differences in detail:
Other types of power supply units are:
This special category of power supply units is designed to be accommodated in 19" racks. These racks are used in various industries and applications for the assembly of electronic devices, servers, audio and video equipment and other components. Standardisation refers to the width of the enclosure that is mounted in a rack. A typical 19" rack can accommodate various devices that can be mounted in this standardised width and height to enable a compact and structured arrangement of equipment. 19" power supply units are specially manufactured to fit into such racks. They can include different types of power supply such as power supply units, voltage converters, power supplies with different output voltages or special power supplies for specific applications. This type of power supply is often used in professional environments, data centres, laboratories and in industry, where a structured and standardised assembly of electronic devices is required. The 19" standard makes it easier to install, maintain and replace components, as they can simply be installed in the racks provided.
A modular power supply unit consists of various modular components such as input modules, output modules, control modules, communication modules, etc. These modules can be replaced, added, or removed separately in order to change or expand the specifications of the power supply unit. The ability to combine or exchange modules means that modular power supply units can be adapted to changing requirements and to a wide range of voltage and current requirements - for example, by using modules with different output voltages or currents. In the event of a defect or maintenance, modules can be easily replaced without having to replace the entire power supply unit. Modular power supply units also often offer greater reliability, as failures of individual modules do not necessarily affect the functionality of the entire power supply unit. They can also offer improved energy efficiency as modules can be added or removed as required. Depending on the requirements, modular power supply units can adopt different configurations by combining modules to fulfil functions such as increased output power, multiple output voltages or special control and monitoring functions. Modular power supply units are used, for example, in industry, telecommunications, laboratories and test environments, as well as in applications where flexible and customisable power supply solutions are required.
They are specially designed to be integrated into other devices, systems or structures. They often take the form of a housing or a packaged module and can be welded into a pre-assembled circuit board that can be inserted into the circuit. With built-in power supply units, some power supply units have a limited output voltage variance, for example: B. 11 V to 16 V. The power range is up to 5,000 W. These devices are very compact in order to save space.
DIN rail power supply units
These power supply units have been specially developed for mounting on DIN rails. DIN rails are standardised metal rails that are used in electrical enclosures, among other things, to mount electronic components, including power supply units. These power supply units are housed in compact, modular enclosures and are often used in industrial applications, control systems, automation solutions and other areas where a reliable power supply is required. Many DIN rail power supply units are designed for a wide range of input voltages in order to adapt to different electrical systems. They are available in several performance classes to meet different requirements. Some DIN rail power supply units have monitoring and protection functions such as overload protection, short-circuit protection and overvoltage protection.
Power supply units can be connected in series, but you should note the following:
If you connect power supply units in series, the output voltages of the individual devices add up. Ensure that the total voltage is within the limits of the connected load and does not exceed the permissible operating voltages.
The total current flowing through the series-connected power supply units remains constant. Check the specifications to ensure that the current load of each individual power supply unit and the total current load do not exceed the permissible limits.
Not all power supply units are suitable for operation in series. Some devices may not function properly when connected in series due to differences in regulation or stability of the output voltage.
Check the safety standards and regulations to ensure that connecting power supply units in series does not pose any safety risks, such as exceeding voltage limits or the occurrence of faults that could damage the devices.
Always follow the instructions and specifications of the power supply unit manufacturer and consult your dataTec experts if you are unsure.
Power supply units can be connected in parallel to supply a higher total current. Please note the following:
Depending on the type and model, power supply units offer different programming options.
Laboratory power supplies offer a variety of interface options that allow them to be controlled, programmed, and connected to other devices or systems, including:
You should ask yourself the following questions before buying a power supply unit:
The primary power supply specifications are the voltage and current output parameters. In terms of voltage, the power supply unit can have a fixed or variable output. If it has a fixed output, you can achieve the desired value with a small setting. If the power supply has a variable range, ensure that the power supply unit covers the required range. In terms of current, the power supply unit must be able to supply the required power. It should also have a certain amount of leeway beyond this minimum requirement. When calculating the requirements for the power supply specification, the so-called inrush current must be taken into account. When an appliance is switched on, a large current surge is initially drawn to charge capacitors. This inrush current can be a multiple of the normal operating current.
"Grid control" (also referred to as "mains voltage control" or "mains voltage tolerance") is a parameter in the specifications of power supply units that describes the ability of a power supply unit to provide a stable output voltage, regardless of fluctuations or variations in the input mains voltage. The grid control specifies how much the output voltage of the power supply changes when the input mains voltage changes. The grid control specification is normally given in millivolts for a specific input variation. It can also be quantified as a percentage of the output voltage. For most power supply units, it should be a few millivolts (e. g. 5 mV) or around 0.01 % of the maximum output voltage for a change in the mains voltage within the operating range.
Good grid control is important to ensure that the connected devices or circuits receive a stable and reliable supply of the required voltage, regardless of fluctuations or irregularities in the input mains voltage.
Load control is a parameter that is included in the specifications of power supplies. It indicates how much the output voltage of the power supply fluctuates when the connected load changes. Power fluctuations are normally expressed as millivolt fluctuations or as a percentage of the maximum output voltage. With a gradual load change from 0 to 100 %, this can be a few millivolts (e. g. 5 mV) or 0.01 %. It is normally specified as constant supply voltage and constant temperature. The voltage on the line from the power supply to the load may also drop. This can be reduced by using thicker wires with lower resistance.
With remote monitoring, the power supply unit is connected to the load, but additional wires are used to measure the voltage at the load. These wires carry almost no current. They are much thinner and there is almost no voltage drop along the wires. They detect the voltage at the load and feed this information back to the power supply unit so that the voltage regulator circuit regulates the voltage at the load instead of the output of the power supply unit. This function upgrades a power supply unit.
Some questions can be answered easily and directly on the phone. Just call us. Our experts will be happy to assist you.

