#statusMessage#
Do you want to start the comparison now?
#statusMessage#
Do you want to start the comparison now?
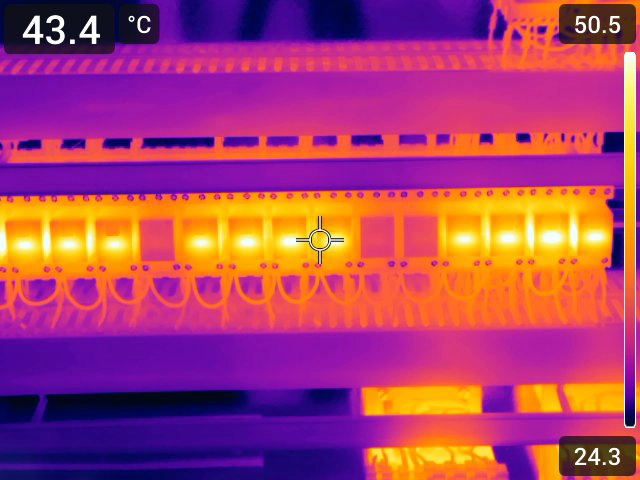

How Thermography Enhances Manufacturing. Machine stoppages, component overheating, or electrical faults—unplanned downti...

Disturbances in the power grid often go unnoticed until systems shut down or equipment fails. Regular power quality asse...

In this practical checklist you will learn how to calibrate your measuring and test instruments effectively – simply, ef...
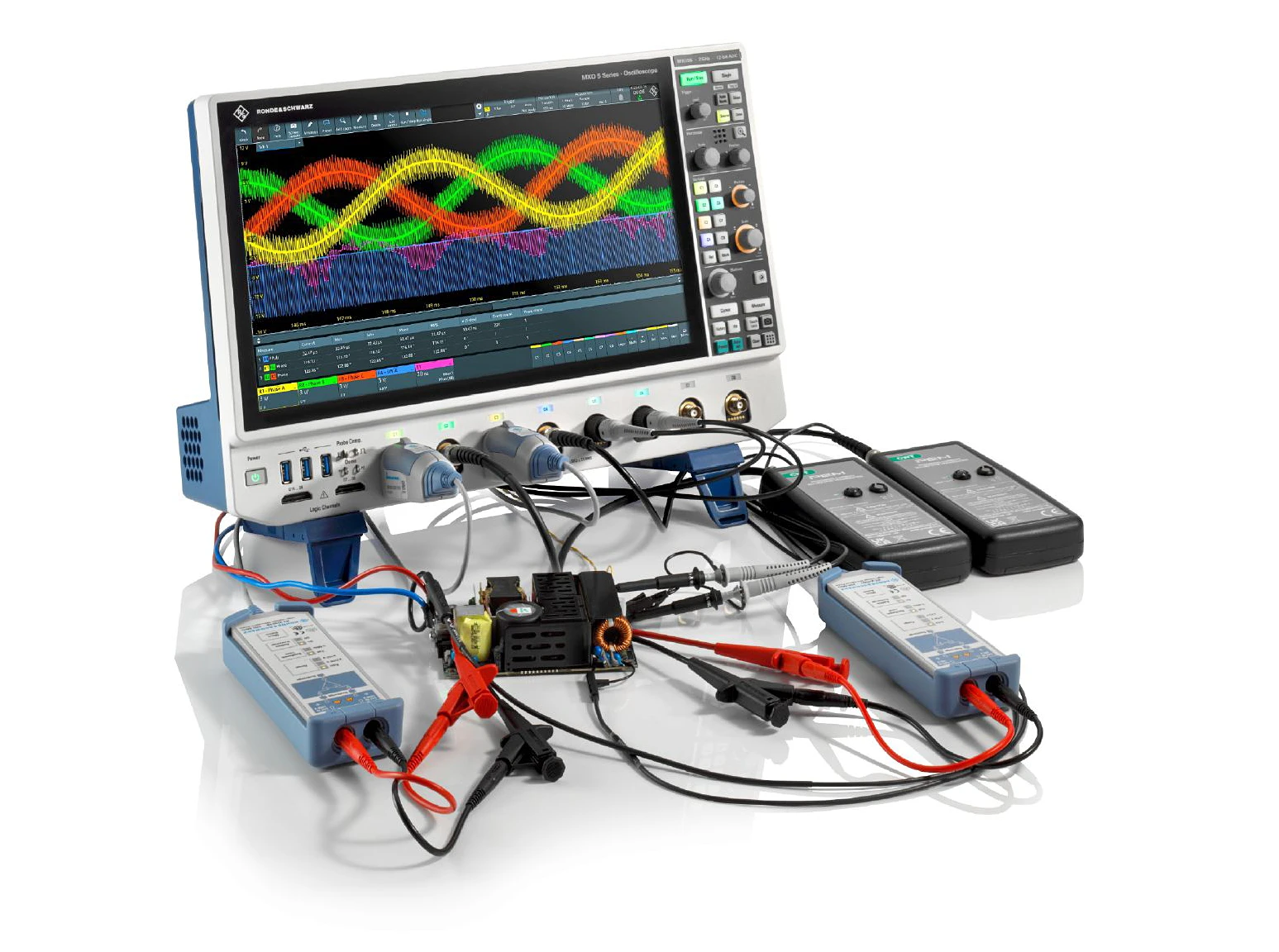
Modern oscilloscopes of the MXO Series from Rohde & Schwarz enable precise analysis and optimization of electric drivetr...
.png)
Discover our selection of thermal imaging cameras / infrared cameras, temperature measurement devices and endoscopes that help you find hotspots and defects of electrical or mechanical industrial equipment at an early stage. Select thermographic measurement technology for instant diagnostic results in research & development (RD), automation, industrial safety monitoring or in energy consulting in the building trade here in our Thermography category.
Our guide supports you in selecting the right thermal imaging device for your needs.
What Is a Thermal Imaging Device?
A thermal imaging device makes infrared radiation—normally invisible to the human eye—visible. It allows for the measurement of surface temperatures on objects using a non-contact method. Thermal imaging cameras or infrared thermometers are used to detect hotspots that can lead to failure in electrical or mechanical systems. For example, electrical panels and motor control centers are frequently inspected using thermal cameras. Early detection of problem areas can prevent production downtime and save costs. The measurement technology converts invisible infrared radiation into electrical signals.
The range of available thermal imaging cameras varies from low-cost, user-friendly devices to highly specialized HD models for scientific research. This ensures the right solution for every requirement.
Isolated parameters like temperature, rotation speed, sound levels, and illumination usually require dedicated instruments for accurate measurement.
At dataTec, we help you choose the right thermal imaging device. Our experts provide independent, non-binding advice. Ask us for a recommendation via our contact form or give us a call—we’ll help you make the right choice for your business.
Applications of Thermal Imaging
Thermal imaging technology can be used in a wide range of sectors. It’s commonly applied in automotive diagnostics, building inspections, and electrical system monitoring. Heat loss and water damage can also be detected using thermal imaging.
Thermal imaging plays an important role in infection control. Thermal cameras are used to detect elevated body temperatures as potential indicators of viral infections. They help break infection chains by identifying individuals with fever quickly and without contact.
Active and Passive Thermal Imaging
In active thermal imaging, thermal impulses are actively applied to the measurement object—usually just a few tenths of a degree Celsius. The heat penetrates the object. Any irregularity in heat conduction results in longer surface warmth, which is captured by the camera.
Passive thermal imaging does not require an external heat source. It measures the natural temperature distribution of an object’s surface.
Applications for Active Thermal Imaging
Used to detect bonding issues, cracks, delaminations, air pockets, or corrosion. It’s also useful for assessing welds, adhesive joints, and soldered connections.
Applications for Passive Thermal Imaging
Used in quality control in plastics industries, such as automotive, electronics, and healthcare. Also applied in construction to detect thermal bridges.
What Are the Advantages of an Infrared Camera?
Easy operation, full scene representation, clear visualization of problems, and data storage. The camera pinpoints exactly what needs repair.
Thermographic Testing and Standards
Thermal testing of electrical systems is mandatory under DIN 54191 and is regularly conducted to ensure fire safety and functionality in industrial settings. Cameras quickly detect issues. If a system passes, it receives a certified inspection label indicating the next due date. Inspection frequency depends on the system’s size and complexity.
Training under DIN 54162 is relevant for energy consultants, construction defect assessors, architects, engineers, contractors, building biologists, and insurance professionals. The course covers regulations, measurement principles, IR camera operation, image analysis, and documentation practices.
Certification is issued by TÜV, confirming qualification as a "Thermography Specialist (TÜV) according to DIN 54162 and EN 473."
These factors are essential when buying a thermal imaging device. Consider the following:
These are among the most recognized manufacturers in the thermal imaging industry.
Do I Need Software or Special Programs?
Depending on the device’s design and use case, software or adapters may be required. Our experts can help you find the right accessories.
Overlaying real images onto thermal images enhances spatial awareness, especially on PCBs.
Advanced software enables automatic measurement analysis and long-term data recording, including temperature profiles and cross-sectional evaluations.
dataTec offers a variety of theory and hands-on seminars in thermal imaging to teach image interpretation, measurement documentation, and system handling.

